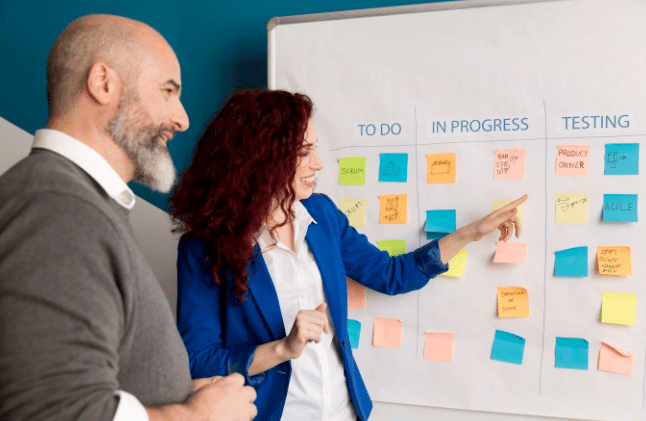
Designing physical products involves a series of structured steps where each stage builds on the previous one. Decisions made early in the process often influence the direction and outcome of the final product. Introducing feedback tools at specific points in the design lifecycle supports a more informed development process and encourages steady progress across phases.
Choosing the right time to use design feedback tools for physical product development helps connect product function with user needs. If used too late, they may lead to rushed changes. If used too early without structure, they may offer little value. Here are the key stages where feedback tools can guide progress without causing delays.
Early Ideation and Concept Exploration
Initial planning starts with rough concepts, potential solutions, and assumptions. Sketches, design prompts, and initial outlines allow teams to explore a range of directions without being tied to a fixed path. Introducing feedback tools in this phase enables open-ended discussions about feasibility, need, and alignment. Early conversations with cross-functional teams or focus groups can reveal blind spots and provide a broader perspective before decisions are finalized.
Building Prototypes and Draft Models
With a clear plan, teams start building early versions of the product. These rough models bring ideas into a visible form. They help show shape and function in simple ways. During this phase, basic tests are conducted to verify fit, scale, and ease of use. The models don’t need to be final, just detailed enough to gather feedback. Teams often observe how users interact with the prototype and note their responses through brief, focused conversations.
Iterative Refinement and Adjustment
As the design matures, this phase focuses on shaping finer details rather than broad concepts. Teams focus on enhancing functionality, refining user interactions, and ensuring that all elements work together seamlessly as intended. Several feedback methods are introduced to examine the product’s developing structure.
- Structured reviews help identify subtle inconsistencies
- Task-based trials can highlight hidden user preferences
- Internal walkthroughs can test clarity in product use
Pre-Launch Assessment and Final Testing
Before moving forward with production, final versions are created to simulate real-world conditions. The focus shifts from shaping the product to validating its readiness. This includes testing performance, checking tolerances, and reviewing consistency. Final testing involves input from internal teams, production partners, and select users. Observing how the product performs in a full-use scenario ensures stability. At this point, feedback tools help document recurring patterns and collect opinions on packaging, assembly, and use.
Post-Release Observation and Evaluation
After launch, attention turns to how the product is received over time. Even after the design is complete, user feedback continues to play a role in identifying opportunities for updates or future improvements. User input collected after release reflects long-term interaction and satisfaction. Feedback tools used here may include experience surveys, observational studies, and data analytics. These inputs support future planning while maintaining awareness of product performance beyond the development stage.
How to Find the Right Space for Design Feedback
In the development of any business, organizing feedback is vital. A clear and consistent setup allows teams to review design files, leave notes, and track progress without confusion. The right environment supports communication without slowing down the pace of work. Selecting a tool that includes visual collaboration and version tracking makes it easier to keep input focused and organized. It also helps reduce repeated tasks and keeps all updates in view. Bringing revisions, comments, and team discussions into one place supports better decisions without complicating the process.
Introducing design feedback tools for physical product development at consistent and well-timed stages encourages thoughtful progression from idea to completion. Tools serve different purposes across phases. These tools offer insight that supports both direction and clarity without disrupting the natural flow of the design lifecycle. This structured approach streamlines collaboration and helps teams catch potential issues early, reducing costly revisions later in the process.